Evidence based medicine nandinii080100332
-
Upload
nandinii-ramasenderan -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
1.452 -
download
1
Transcript of Evidence based medicine nandinii080100332

EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE (EBM)
Nandinii Ramasenderan080100332

OVERVIEW Definition History Factors driving EBM Steps in EBM Case discussion

WHAT IS EBM?A systematic approach to clinical problem solving which allows the integration of the best available research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values
-Dave Sackett-
Patient Concerns
Clinical Expertise
Best research evidence
EBM

INTEGRATED WITH CLINICAL EXPERTISE

RISE OF EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE


LIFE LONG LEARNINGThe hardest conviction to get into the mind of a beginner is that the education upon which he is engaged is not … a medical course, but a life course, for which the work of a few years under teachers is but a preparation.
Sir William Osler (1849-1919), from: The Student of Medicine

STEPS IN PRACTISING EBM

STEP 1 : FORMULATE QUESTION Background Question-Ask for general knowledge about a condition or thing-Have 2 essential components:a)A question root (who, what, where, when how, why) and a verbb)A disorder, test, tx, or other aspect of health care.Eg: -how does heart failure cause ascites? -what causes SARS?

STEP 1 : FORMULATE QUESTION Foreground Question-Ask for specific knowledge to inform clinical decision / actions-4 essential components:a)Patient and /or problemb)Intervention (or exposure)c)Comparison, if relevantd)Outcome (clinical), including time if relevantEg: “ In adults with heart failure who are in sinus rhythm, would adding warfarin to standard therapy reduce morbidity or mortality from thromboembolism enough over 3-5 years to be worth warfarin’s harmful effects and inconveniences.”

BACKGROUND
FOREGROUND
TYPE OF QUESTION
CLINICAL EXPERIENCE
STEP 1 : Formulate QuestionThe nature of the question asked is critically experience dependent.

STEP 2: USE BEST EVIDENCE TO ANSWER QUESTION
Computerized decision support system (CDSS)
Evidence-based journal abstracts
Cochrane reviews
Original published articles in journals

STEP 2: USE BEST EVIDENCE TO ANSWER QUESTION
System-Evidence based clinical information, researches
-Electronic basedBMJ Clinical Evidence (http://www.clinicalevidence.com)UpToDate (http://www.uptodate.com)PIER: The Physician’s Information and Education Resource (http://pier.acponline.org/index.html).
Synopses-A brief summary/ review of individual studies
-Provide only information to support a clinical actionACP [American College of Physicians] Journal Club(http://www.acpjc.orgEBM (http://ebm.bmj.com).

STEP 2: USE BEST EVIDENCE TO ANSWER QUESTION
Syntheses-summaries of articles/ reviews The Cochrane Library Web site (http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/ cgibin/mrwhome/106568753/HOME)DARE(www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd/welcome.htm)
Studies-original research journalMedline/ PubMed Clinical Queries (www.pubmed.com)EMBASE (OVID) (www.ovid.com)

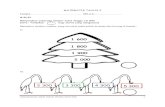
HIERARCHY OF EVIDENCE PYRAMID

LEVEL OF EVIDENCE Level type of investigation
IaIa Evidence obtained from meta analysis of Evidence obtained from meta analysis of randomized controlled trialsrandomized controlled trials
IbIb Evidence obtained from at least one Evidence obtained from at least one randomized controlled trialrandomized controlled trial
IIaIIa Evidence obtained from at least one well Evidence obtained from at least one well designed controlled study without designed controlled study without randomizationrandomization
IIbIIb Evidence obtained from at least one other Evidence obtained from at least one other type of well designed quasi experimental type of well designed quasi experimental studystudy
IIIIII Evidence obtained from well designed non Evidence obtained from well designed non experimental studies, such as comparative experimental studies, such as comparative studies, correlational studies, and case studies studies, correlational studies, and case studies
IVIV Evidence obtained from expert committee Evidence obtained from expert committee reports or opinionsreports or opinions

STEP 3: CRITICALLY APPRAISE EVIDENCE
To understand the methods and results of research and to assess the quality of the researchTHREE MAIN ASPECTS TO BE APPRAISED: V I A
1. VALIDITY : VALID (CLOSENESS TO THE TRUTH) IN THE METHODOLOGY SECTION
2. IMPORTANCE :IMPORTANT (USEFULNESS) IN THE RESULTS SECTION
3. APPLICABILITY :APPLICABLE (CAN BE APPLIED IN CLINICAL PRACTICE) IN THE DISCUSSION SECTION

STEP 4: INTEGRATE FINDINGS INTO PRACTISE Making a concise decision based on research finding & information found.Discuss with patient regarding our findings & risk-benefit assessment

CASE DISCUSSION

68 years old Malay FemaleHx of Congestive Heart Failure & HypertensionSurgical Hx: CABG 10 years agoOn medication: Digoxin, Lasix, Isosorbide nitrateMild increase of dysnea on exertion past 4 daysHaving acute Shortness of breath 1hour prior to admission

On examination: BP: 188/104 mmHg Pulse rate:122 bpmRespiratory rate: 30 Temp: 37.5 CelsiusSpO2: 90% (On Non-rebreather mask)Lung auscultation: Crackles to ½ bilateralJugular vein distended, S3 gallopPretibial edema bilaterally

PLAN & INVESTIGATIONIV, O2, & vital sign MonitoringChest Xray, ECG, Cardiac markers, Digoxin levelECG: Sinus tachycardia, old inferior myocardial infarction, no st-elevation changesCXR: acute pulmonary edema (pulmonary venous congestion, small bilateral effusion)TreatmentGTNLasixMorphine

QUESTION—GENERAL STATEMENT What about using ACE inhibitors for acute pulmonary edema?

BACKGROUNDDescribe pathophysiology of CHF and acute pulmonary edemaDiscuss causes of decompensation of CHFDiscuss Differential Diagnosis of acute pulmonary edemaRelate pathophysiology of CHF to treatment, especially role of ACE-I in CHFDescribe treatment goalsDescribe standard treatment of CHF

EBM QUESTION Patients: Acute Pulmonary Edema Intervention: ACE Inhibitor Comparison: Placebo Outcome: Mortality Intubation Hemodynamic parameters ICU/CCU admission







THANK YOU