Klasifikasi Tanah
description
Transcript of Klasifikasi Tanah

DASAR ILMU TANAH
Klasifikasi TanahKlasifikasi Tanah

KLASIFIKASI TANAHKLASIFIKASI TANAH

Klasifikasi TanahUsaha membeda-bedakan
mengelompokkan tanah berdasarkan sifat-sifatnya
Tujuan mengetahui sifat dan ciri tanah pada masing-
masing kelompok tanah (kelas tanah) sehingga memudahkan pengguna tanah untuk mengelola tanah tersebut agar dapat berproduksi secara optimal

Alami/taksonomi:berdasarkan sifat2 alami tanah tanpa dihub. dgn pengunaannya
- Taksonomi Tanah (USDA)
Teknikal: berdasarkan tujuan khusus dgn memilih ciri2 ttt yg pgrhi kemampuan dan penggunaannya- - Klasifikasi Kemampuan Lahan USDA- - Klasifikasi Kesesuaian Lahan FAO
Klasifikasi

Why Classify Soils?• Organize knowledge to enable
investigation and communication (structure/organization)
• Provide framework for establishing relationships among soils and their environment (scientific)
• Establish groupings for interpretations (utilitarian)– Optimal use
– Hazard/limitation/remediation assessment
– Potential productivity
– Framework for technology transfer/information dissemination

Tanah bermacam-macam

Klasifikasi Tanah di IndonesiaKlasifikasi Tanah di Indonesia
Sejak th 1988 hanya gunakan Sejak th 1988 hanya gunakan sistem Taksonomi Tanah. sistem Taksonomi Tanah.
Sebelum 1988 ada 3Sebelum 1988 ada 3 : :
- - Pusat Penelitian Tanah Pusat Penelitian Tanah (PPT) (PPT)
- FAO/UNESCOFAO/UNESCO- Taksonomi TanahTaksonomi Tanah..

Taksonomi Tanah (USDA)
dikembangkan oleh Soil Survey Staff (USDA), tahun 1975 Terus direvisi 2ed, 1999
ada 6 kategori yaitu Order, Suborder, Great group, Subgroup, Family dan Series.

Categories in ST:Categories in ST: OrderOrder – key soil properties resulting from major soil- – key soil properties resulting from major soil-
forming processes (epipedons, subsurface horizons, forming processes (epipedons, subsurface horizons, materials, characteristics)materials, characteristics)
SuborderSuborder – key soil properties that are major controls on – key soil properties that are major controls on soil-forming processes, e.g., soil climate (most orders); soil-forming processes, e.g., soil climate (most orders); kinds of salts (Aridisols); kinds of soil parent materials kinds of salts (Aridisols); kinds of soil parent materials (Entisols); degree of decomposition (Histosols); presence (Entisols); degree of decomposition (Histosols); presence or absence of cryoturbation (Gelisols)or absence of cryoturbation (Gelisols)
Great GroupGreat Group – key soil properties that are additional – key soil properties that are additional controls on soil genesis (diagnostic horizons)controls on soil genesis (diagnostic horizons)
SubgroupSubgroup – central concept (Typic), intergrades, – central concept (Typic), intergrades, extragradesextragrades
FamilyFamily – properties important to plant growth (texture, – properties important to plant growth (texture, mineralogy, soil temperature regime, etc.)mineralogy, soil temperature regime, etc.)
SeriesSeries – soil morphology – soil morphology

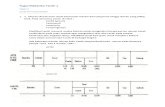
KategoKategoriri
NamaNama KategoriKategori NamaNama
PhylumPhylum PteridophytaPteridophyta OrderOrder AlfisolAlfisol
KelasKelas AngiospermaAngiospermaee
Sub-orderSub-order UdalfUdalf
Sub-Sub-kelaskelas
DicotyledoneDicotyledoneaeae
GreatgrouGreatgroupp
HapludalfHapludalf
OrderOrder RosalesRosales Sub-groupSub-group Aquic HapludalfAquic Hapludalf
FamilyFamily LeguminoseaLeguminoseaee
FamilyFamily Aquic Hapludalf, berlempung Aquic Hapludalf, berlempung halus, Campuran, Aktif, halus, Campuran, Aktif, Isohipertermik Isohipertermik
GenusGenus TrifoliumTrifolium SeriSeri LapeLape
SpeciesSpecies T. repensT. repens ((Phase)Phase) BerbatuBerbatu

Differentiating Characteristics in Differentiating Characteristics in STST::
Diagnostic epipedons Diagnostic epipedons Diagnostic subsurface horizons Diagnostic subsurface horizons Other diagnostic soil characteristics Other diagnostic soil characteristics Soil moisture and temperature Soil moisture and temperature
regimes regimes

1. Epipedon1. Epipedon
horison penciri yg terbentuk di horison penciri yg terbentuk di permukaan tanah. permukaan tanah.
tidak sinonim dg horizon Atidak sinonim dg horizon Adapat mencakup sebagian dapat mencakup sebagian
horizon B. horizon B.

EPIPEDONEPIPEDON
Surface horizonsSurface horizons Influenced strongly by Influenced strongly by
biochemical and biochemical and geochemical processesgeochemical processes
Correspond with A, E, and Correspond with A, E, and sometimes upper B horizonssometimes upper B horizons
Important in classifying soilsImportant in classifying soils

EPIPEDONEPIPEDON HistikHistik: : Bahan organik (BO) tinggi (>75%), tebal 20‑40cm.Bahan organik (BO) tinggi (>75%), tebal 20‑40cm. MollikMollik: : BO >1%, warna gelap dg value dan kroma <3 BO >1%, warna gelap dg value dan kroma <3
(lembab) dan value < 5 (kering), tebal >18cm, KB (lembab) dan value < 5 (kering), tebal >18cm, KB >50%.>50%. MelanikMelanik: : mirip Mollik,mirip Mollik, tetapi tetapi miliki sifat tanah andik miliki sifat tanah andik UmbrikUmbrik: : seperti molik seperti molik tetapitetapi KB <50%. KB <50%. AnthropikAnthropik: : seperti molik, seperti molik, tetapitetapi mengandung >1500 ppm P2O5 mengandung >1500 ppm P2O5
larut dalam 1% as sitrat. larut dalam 1% as sitrat. OchrikOchrik: : warna terang (value dan kroma lembab >3), BO warna terang (value dan kroma lembab >3), BO
<1% atau keras‑sangat keras dan masif.<1% atau keras‑sangat keras dan masif. PlaggenPlaggen: : horizon buatan, akibat penggunaan pupuk kandang horizon buatan, akibat penggunaan pupuk kandang
yg yg terus menerus, tebal >50cm, berwarna hitam.terus menerus, tebal >50cm, berwarna hitam. FolistikFolistik: : tanah atas BO, jenuh < 30 haritanah atas BO, jenuh < 30 hari

Horison Penciri BawahHorison Penciri Bawah AgrikAgrik: : horizon iluviasi yg terbentuk krn pengaruh horizon iluviasi yg terbentuk krn pengaruh
pengolahan tanah shg terjadi akumulasi sejumlah pengolahan tanah shg terjadi akumulasi sejumlah debu, debu, liat, dan liat, dan humus.humus.
AlbikAlbik: : horison berwarna pucat (E) dg value lembab >5.horison berwarna pucat (E) dg value lembab >5. ArgillikArgillik: : horison penimbunan liat; minimal mengandung horison penimbunan liat; minimal mengandung
liat liat >1.2 kali lebih banyak daripada kandungan liat di >1.2 kali lebih banyak daripada kandungan liat di atasnya.Terdapat selaput liat.atasnya.Terdapat selaput liat.
KalsikKalsik: : horizon yg mengandung karbonat sekunder horizon yg mengandung karbonat sekunder (CaCO(CaCO33 atau MgCO atau MgCO33) tinggi, tebal >15cm.) tinggi, tebal >15cm.
PetrokalsikPetrokalsik:: horizon kalsik yang mengeras.horizon kalsik yang mengeras. KambikKambik: : indikasi lemah adanya argillik atau spodik, tapi indikasi lemah adanya argillik atau spodik, tapi
tidak tidak memenuhi syarat kedua horizon tersebut.memenuhi syarat kedua horizon tersebut.

Horison Penciri Bawah (lanjutan)Horison Penciri Bawah (lanjutan)
GipsikGipsik : : banyak mengandung gipsum (CaSO4) sekunder.banyak mengandung gipsum (CaSO4) sekunder. PetrogipsikPetrogipsik:: horizon gipsik yg mengeras.horizon gipsik yg mengeras. NatrikNatrik : : horizon argillik yg banyak mengandung Nahorizon argillik yg banyak mengandung Na OksikOksik : : horizon bertekstur agak kasar, KTK <16 me/100g horizon bertekstur agak kasar, KTK <16 me/100g
liat, liat, tebal >30cm.tebal >30cm. SalikSalik: : banyak mengandung garam sekunder mudah larut, banyak mengandung garam sekunder mudah larut,
tebal >15cm.tebal >15cm. SombrikSombrik : : seperti umbrik, gelap, terjadi iluviasi humus tanpa Al, seperti umbrik, gelap, terjadi iluviasi humus tanpa Al,
tidak terletak di bawah horizon albik.tidak terletak di bawah horizon albik. SpodikSpodik : : horizon iluviasi seskuioksida bebas dan BO.horizon iluviasi seskuioksida bebas dan BO. SulfurikSulfurik : : horizon yg mengandung sulfat, pH ,3.5, tdpt karatan horizon yg mengandung sulfat, pH ,3.5, tdpt karatan
jarosit. jarosit. PlasikPlasik: : padas tipis tersementasi senyawa. Fe, Mn dan BOpadas tipis tersementasi senyawa. Fe, Mn dan BO

KategoKategoriri
NamaNama KategoriKategori NamaNama
PhylumPhylum PteridophytaPteridophyta OrderOrder AlfisolAlfisol
KelasKelas AngiospermaAngiospermaee
Sub-orderSub-order UdalfUdalf
Sub-Sub-kelaskelas
DicotyledoneDicotyledoneaeae
GreatgrouGreatgroupp
HapludalfHapludalf
OrderOrder RosalesRosales Sub-groupSub-group Aquic HapludalfAquic Hapludalf
FamilyFamily LeguminoseaLeguminoseaee
FamilyFamily Aquic Hapludalf, berlempung Aquic Hapludalf, berlempung halus, Campuran, Aktif, halus, Campuran, Aktif, Isohipertermik Isohipertermik
GenusGenus TrifoliumTrifolium SeriSeri LapeLape
SpeciesSpecies T. repensT. repens ((Phase)Phase) BerbatuBerbatu
TAKSONOMI TUMBUHAN vs TAKSONOMI TANAH

““Soil TaxonomySoil Taxonomy""
Degree of Weathering and B Horizon DevelopmentDegree of Weathering and B Horizon Development
LittleLittle SlightSlight ModerateModerate LargeLarge ExtremeExtreme
EntisolsEntisols AridisolsAridisols
InceptisolsInceptisols AlfisolsAlfisols
SpodosolsSpodosols UltisolsUltisols
MollisolsMollisols OxisolsOxisols
Soils Defined by Special Constituent MaterialsSoils Defined by Special Constituent Materials
AndisolsAndisols Volcanic AshVolcanic Ash
HistosolsHistosols Peat, Organic MatterPeat, Organic Matter
VertisolsVertisols ““Self-Mixing” Clay SoilsSelf-Mixing” Clay Soils
GelisolsGelisols Soils on PermafrostSoils on Permafrost

ALFISOLALFISOL
The central concept of Alfisols The central concept of Alfisols is that of soils that have an is that of soils that have an argillic, a kandic, or a natric argillic, a kandic, or a natric horizon and a base saturation horizon and a base saturation of 35% or greater. of 35% or greater.
They typically have an ochric They typically have an ochric epipedon, but may have an epipedon, but may have an umbric epipedon. They may umbric epipedon. They may also have a petrocalcic horizon, also have a petrocalcic horizon, a fragipan or a duripan. a fragipan or a duripan.

ANDISOLSANDISOLS
The central concept of The central concept of Andisols is that of soils Andisols is that of soils dominated by short-range-dominated by short-range-order minerals. order minerals.
They include weakly They include weakly weathered soils with much weathered soils with much volcanic glass as well as more volcanic glass as well as more strongly weathered soils. strongly weathered soils.
Hence the content of volcanic Hence the content of volcanic glass is one of the glass is one of the characteristics used in defining characteristics used in defining andic soil properties andic soil properties

ARIDISOLAridisols is that of soils that are too dry for mesophytic plants to grow. They have either: (1) an aridic moisture regime and an ochric or anthropic epipedon and one or more of the following with an upper boundry within 100 cm of the soil surface: a calcic, cambic, gypsic, natric, petrocalcic petrogypsic, or a salic horizon or a duripan or an argillic horizon, or (2)A salic horizon and saturation with water within 100 cm of the soil surface for one month or more in normal years.

ENTISOLSENTISOLS
The central concept of The central concept of Entisols is that of soils that Entisols is that of soils that have little or no evidence of have little or no evidence of development of pedogenic development of pedogenic horizons. horizons.
Many Entisols have an ochric Many Entisols have an ochric epipedon and a few have an epipedon and a few have an anthropic epipedon. Many anthropic epipedon. Many are sandy or very shallow. are sandy or very shallow.

GELISOLSGELISOLS
The central concept of Gelisols is that The central concept of Gelisols is that of soils that have permafrost within of soils that have permafrost within 100 cm of the soil surface and/or 100 cm of the soil surface and/or have gelic materials within 100 cm of have gelic materials within 100 cm of the soil surface and have permafrost the soil surface and have permafrost within 200 cm. within 200 cm.
Gelic materials are mineral or organic Gelic materials are mineral or organic soil materials that have evidence of soil materials that have evidence of cryoturbation (frost churning) and/or cryoturbation (frost churning) and/or ice segeration in the active layer ice segeration in the active layer (seasonal thaw layer) and/or the (seasonal thaw layer) and/or the upper part of the permafrost. upper part of the permafrost.

HISTOSOLSHISTOSOLS The central concept of Histosols is The central concept of Histosols is
that of soils that are dominantly that of soils that are dominantly organic. They are mostly soils that organic. They are mostly soils that are commonly called bogs, moors, are commonly called bogs, moors, or peats and mucks. or peats and mucks.
A soil is classified as Histosols if it A soil is classified as Histosols if it does not have permafrost and is does not have permafrost and is dominated by organic soil dominated by organic soil materials. materials.

INCEPTISOLS INCEPTISOLS The central concept of The central concept of
Inceptisols is that of soils of Inceptisols is that of soils of humid and subhumid regions humid and subhumid regions that have altered horizons that that have altered horizons that have lost bases or iron and have lost bases or iron and aluminum but retain some aluminum but retain some weatherable minerals. They do weatherable minerals. They do not have an illuvial horizon not have an illuvial horizon enriched with either silicate clay enriched with either silicate clay or with an amorphous mixture or with an amorphous mixture of aluminum and organic of aluminum and organic carbon. carbon.
The Inceptisols may have many The Inceptisols may have many kinds of diagnostic horizons, but kinds of diagnostic horizons, but argillic, natric kandic, spodic argillic, natric kandic, spodic and oxic horizons are excluded. and oxic horizons are excluded.

MOLLISOLSMOLLISOLS The central concept of Mollisols is The central concept of Mollisols is
that of soils that have a dark that of soils that have a dark colored surface horizon and are colored surface horizon and are base rich. Nearly all have a mollic base rich. Nearly all have a mollic epipedon. epipedon.
Many also have an argillic or Many also have an argillic or natric horizon or a calcic horizon. natric horizon or a calcic horizon. A few have an albic horizon. A few have an albic horizon. Some also have a duripan or a Some also have a duripan or a petrocalic horizonpetrocalic horizon. .

OXISOLS OXISOLS The central concept of Oxisols is The central concept of Oxisols is
that of soils of the tropical and that of soils of the tropical and subtropical regions. They have subtropical regions. They have gentle slopes on surfaces of great gentle slopes on surfaces of great age. They are mixtures of quartz, age. They are mixtures of quartz, kaolin, free oxides, and organic kaolin, free oxides, and organic matter. matter.
For the most part they are nearly For the most part they are nearly featureless soils without clearly featureless soils without clearly marked horizons. Differences in marked horizons. Differences in properties with depth are so properties with depth are so gradual that horizon boundaries gradual that horizon boundaries are generally arbitrary. are generally arbitrary.

SPODOSOLS SPODOSOLS The central concept of Spodosols is The central concept of Spodosols is
that of soils in which amorphous that of soils in which amorphous mixtures of organic matter and mixtures of organic matter and aluminum, with or without iron, aluminum, with or without iron, have accumulated. In undisrurbed have accumulated. In undisrurbed soils there is normally an overlying soils there is normally an overlying eluvial horizon, generally gray to eluvial horizon, generally gray to light gray in color, that has the color light gray in color, that has the color of more or less uncoated quartz. of more or less uncoated quartz.
Most Spodosols have little silicate Most Spodosols have little silicate clay. The particle-size class is clay. The particle-size class is mostly sandy, sandy-skeletal, mostly sandy, sandy-skeletal, coarse-loamy, loamy, loamy- coarse-loamy, loamy, loamy- skeletal, or coarse-silty. skeletal, or coarse-silty.

ULTISOLSULTISOLS The central concept of Ultisols is The central concept of Ultisols is
that of soils that have a horizon that of soils that have a horizon that contains an appreciable that contains an appreciable amount of translocated silicate amount of translocated silicate clay (an argillic or kandic clay (an argillic or kandic horizon) and few bases (base horizon) and few bases (base saturation less than 35 percent).saturation less than 35 percent).
Base saturation in most Ultisols Base saturation in most Ultisols decreases with depth. decreases with depth.

VERTISOLS VERTISOLS The central concept of The central concept of
Vertisols is that of soils that Vertisols is that of soils that have a high content of have a high content of expending clay and that have expending clay and that have at some time of the year deep at some time of the year deep wide cracks. wide cracks.
They shrink when drying and They shrink when drying and swell when they become swell when they become wetter. wetter.