MAHESWARI.GHANTA
-
Upload
maheswari-srikara-ghanta -
Category
Documents
-
view
120 -
download
3
description
Transcript of MAHESWARI.GHANTA


Presenting By: MAHESWARI.G
Guided By: Prof. Mrs. A .PRAMEELA RANI GARU M. Pharm , Ph.D

Content Introduction Erythrocytes as drug carrier Basic concept of erythrocytes Advantages & limitation Source & Isolation of Erythrocytes Method of drug Loading Drug release, Storage Application Conclusion

Introduction:-
DEF: They are drug -loaded carrier erythrocytes
Idea of drug carrier system
Magic Bullet Concept by PAUL ERLICH

Erythrocytes Erythro= red Cytes = cell
Biconcave discs, anucleate.
Filled with hemoglobin (Hb), a protein that functions in gas transport
Contain the plasma membrane protein spectrin and other proteins that: Give erythrocytes their
flexibility Allow them to change
shape as necessary

Erythrocytes
Healthy adult male= 4.5 millions/µmlHealthy adult female= 4.8 millions/µml
Matured RBCs have no nucleus Ribosome & Mitochondria . Therefore all space is available for drug carrier.
Reticulocytes- immature erythrocytes

Resealed Erythrocytes
Properties as carrier :- Appropriate size, shape. Biocompatible & minimum toxic side effects Minimum leakage before target site is
achieved Should be able to carry broad spectrum of
drugs Appreciable stability during storage period Should have sufficient space & should carry
adequate amounts of drugs

Source, fractionation & isolation of erythrocytes
Source:- mice, cattle, pig, dog, sheep, goat, monkey, chicken, rat, rabbit & human
Whole blood can be collected by venipuncture or from orbital sinus in heparinized tube
Red blood cells can be harvested & centrifuged
Different centrifugal force & different buffer composition for different species is used
Fresh blood is used for loading of drugs.

Membrane perturbation Electroencapsulation Hypoosmotic lysis Lipid fusion endocytosis
Dilution method Preswell method Osmotic lyses method Dialysis method

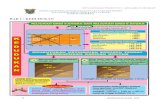
Dilutional Haemolysis
RBC Membrane ruptured RBC Loaded RBC
Resealed Loaded RBC
0.4% NaCl
Hypotonic
Drug
Loading buffer
Resealing buffer
Incubation at 250c
Enzymes delivery
Hypotonic med
Isotonic med.
Washed

Isotonic Osmotic Lysis
RBC Isotonically ruptured RBC
Chemical – urea, polyethylene, polypropylene, and NH4Cl
Physical rupturing
Chemicalrupturing
Drug IsotonicBuffer
Loaded RBC
Resealed RBC
Incubation at 250 C

Preswell Dilutional Haemolysis
RBC 0.6%w/v NaCl Swelled
RBC Drug + Loading buffer
5 min incubation at 0 0c
Loaded
RBC
Incubation at 25 0c
Resealing Buffer
Resealed
RBC
Fig:- Preswell Method

Dialysis
RBC
Phosphate buffer
+ Placed in dialysis bag with air bubble
Dialysis bag placed in 200ml of lysis buffer with mechanical rotator 2hrs. 4c.
DrugLoading buffer
Loaded RBCDialysis bag placed in Resealing buffer with mechanical rotator 30 min 37c.
Resealed RBC

Electro-insertion or Electro-encapsulation
RBC 2.2 Kv Current for 20 micro sec
At 250 CPulsation medium
+ +Drug
Loading suspension
3.7 Kv Current for 20 micro sec
Isotonic NaClLoaded RBC
Resealing Buffer
Resealed RBC
Fig:- Electro-encapsulation Method

Entrapment By Endocytosis:-
RBC
Drug Suspension
+
Buffer containing ATP, MgCl2, and CaCl2
At 250 CLoaded RBC
Resealing Buffer
Resealed RBC
Fig;- Entrapment By Endocytos Method

Membrane perturbation method
RBCAmphotericin B
e.g. Chemical agents
Increased permeability of RBC
Resealing Buffer
Drug
Resealed RBC

Advantages :-Biodegradable & biocompatibleIsolation is easy Non immunogenic
large volume of drug can be encapsulated in small volume of erythrocytesProlong systemic activity of drug
Protection from premature degradation Prodrug concept (Bioreactor) Reduce Adverse Effect Peptide & Enzyme Delivery Disadvantages :-
Possibility of Leakage of cells & dose dumping Molecule Alter Physiology Of cell

Applications of resealed erythrocytesErythrocytes as carrier for enzymes
Erythrocytes as carrier for drugs
Erythrocytes for drug targeting Drug targeting to reticuloendothelial system Drug targeting to liver -Treatment of liver tumors
-Treatment of parasitic diseases -Removal of RES iron overload -Removal of toxic agents

Applications of resealed erythrocytes
Delivery of antiviral agentsOxygen deficiency therapyMicroinjection of macromolecules
Novel systems Nanoerythrosomes Erythrosomes

CONCLUSION:-The use of resealed erythrocytes looks promising for a safe and sure delivery of various drugs for passive and active targeting. However, the concept needs further optimization to become a routine drug delivery and much remains to be explored regarding the potential of resealed erythrocytes

References
Jain.S., Jain.N.K., resealed erythrocytes as drug carriers, Edited Jain N.K., Controlled And Novel Drug Delivery, New Delhi, CBS publishers, New Delhi, 2004, 256-281.
Vyas S.P., Khar R.K., Targeted And Controlled Drug Delivery: Novel Carrier Systems, New Delhi, CBS publisher, 2004, 387-413.
PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY : A Review