c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
-
Upload
suryati-purba -
Category
Documents
-
view
228 -
download
0
Transcript of c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
1/43
MORFOLOGI TANAH
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
2/43
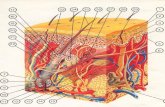
The interaction of the five soil-forming factors; time, climate,parent material, topography,and plant and animal life, resultin the development of a soilprofile.
A soil profile is a vertical section
of the soil beginning at thesurface and extending downinto the unconsolidatedunderlying material to a depthof 60 inches or more.
http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&rct=j&q=soil+morphology&source=images&cd=&cad=rja&docid=64wIdvjOd2JtVM&tbnid=RxmC40I3UyPV7M:&ved=0CAUQjRw&url=http://en.academic.ru/dic.nsf/enwiki/23615&ei=vPg_UdWZKsSBkQXQ4IGoBw&psig=AFQjCNFcbz6QQRLyv8WoDibiwV8tZWbfvQ&ust=1363233298235042 -
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
3/43
http://www.landfood.ubc.ca/soil200/classific
ation/soil_horizon.htm#development
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
4/43
Syarat profil tanah: Baru
Tidak terkena sinar
matahari
Mewakili(representatif)
Tidak Dekat jalan(bahangalian/timbunan)
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
5/43
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
6/43
O Horizon- The top, organic layer of soil, madeup mostly of leaf litter and humus (decomposedorganic matter).
A Horizon- The layer called topsoil; it is foundbelow the O horizon and above the E horizon. Itis made up of humus (decomposed organicmatter) mixed with mineral particles.
E Horizon- This eluviation (leaching) layer islight in color; this layer is beneath the A Horizonand above the B Horizon. It is made up mostly ofsand and silt, having lost most of its minerals andclay as water drips through the soil (in theprocess of eluviation).
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
7/43
B Horizon- This layer is beneath the E Horizonand above the C Horizon. It contains clay andmineral deposits (like iron, aluminum oxides, andcalcium carbonate) that it receives from layers
above it when mineralized water drips from thesoil above.
C Horizon- Also called regolith: the layer beneaththe B Horizon and above the R Horizon. It consistsof slightly broken-up bedrock. Plant roots do not
penetrate into this layer; very little organic materialis found in this layer.
R Horizon- The unweathered rock (bedrock)layer that is beneath all the other layers.
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
8/43
The central concept of
Entisols is that of soils
that have little or no
evidence ofdevelopment of
pedogenic horizons.
Many Entisols have an
ochric epipedon and afew have an anthropic
epipedon. Many are
sandy or very shallow.
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
9/43
The central concept ofInceptisols is that of soilsof humid and subhumidregions that have alteredhorizons that have lostbases or iron and
aluminum but retain someweatherable minerals.They do not have anilluvial horizon enrichedwith either silicate clay or
with an amorphous mixtureof aluminum and organiccarbon.
The Inceptisols may havemany kinds of diagnostichorizons, but argillic, natric
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
10/43
The central concept ofAlfisols is that of soilsthat have an argillic, akandic, or a natrichorizon and a basesaturation of 35% orgreater. They typicallyhave an ochricepipedon, but mayhave an umbricepipedon. They mayalso have a petrocalcic
horizon, a fragipan or a
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
11/43
The central concept ofAndisols is that of soils
dominated by short-range-order minerals. They includweakly weathered soils withmuch volcanic glass as wellas more strongly weathered
soils. Hence the content ofvolcanic glass is one of thecharacteristics used indefining andic soilproperties.
Materials with andic soilproperties comprise 60percent or more of the
thickness between themineral soil surface or the
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
12/43
The central concept of Aridisols isthat of soils that are too dry formesophytic plants to grow. They
have either: (1) an aridic moisture regime and an
ochric or anthropic epipedon and onor more of the following with anupper boundry within 100 cm of thesoil surface: a calcic, cambic, gypsic,natric, petrocalcic petrogypsic, or asalic horizon or a duripan or anargillic horizon, or
(2) A salic horizon and saturation witwater within 100 cm of the soil
surface for one month or more innormal years. An aridic moisture regime is one that
in normal years has no wateravailable for plants for more than halthe cumulative time that the soiltemperature at 50 cm below the
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
13/43
The central concept ofGelisols is that of soils
that have permafrostwithin 100 cm of the soilsurface and/or have gelicmaterials within 100 cm of
the soil surface and havepermafrost within 200 cm.
Gelic materials aremineral or organic soil
materials that haveevidence of cryoturbation(frost churning) and/or icesegeration in the activelayer (seasonal thaw
layer) and/or the upper
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
14/43
The central concept ofHistosols is that of soilsthat are dominantlyorganic. They are mostlysoils that are commonlycalled bogs, moors, orpeats and mucks.
A soil is classified asHistosols if it does nothave permafrost and isdominated by organicsoil materials.
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
15/43
The central concept of
Mollisols is that of soils
that have a dark colored
surface horizon and arebase rich. Nearly all have
a mollic epipedon. Many
also have an argillic or
natric horizon or a calcichorizon. A few have an
albic horizon. Some also
have a duripan or a
petrocalic horizon.
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
16/43
The central concept ofOxisols is that of soils of the
tropical and subtropicalregions. They have gentleslopes on surfaces of greatage. They are mixtures of
quartz, kaolin, free oxides,and organic matter. For themost part they are nearlyfeatureless soils without
clearly marked horizons.Differences in propertieswith depth are so gradualthat horizon boundaries are
generally arbitrary
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
17/43
The central concept ofSpodosols is that of soils in
which amorphous mixtures oforganic matter and aluminum,with or without iron, haveaccumulated. In undisturbedsoils there is normally an
overlying eluvial horizon,generally gray to light gray incolor, that has the color ofmore or less uncoated quartz.
Most Spodosols have littlesilicate clay. The particle-sizeclass is mostly sandy, sandy-skeletal, coarse-loamy, loamy,loamy- skeletal, or coarse-silty
Podzolization : leaching of soluable minerals from A to B horizon typical of cool, humid, and acidic environments
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
18/43
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
19/43
The central concept ofUltisols is that of soils thathave a horizon thatcontains an appreciableamount of translocatedsilicate clay (an argillic orkandic horizon) and fewbases (base saturation
less than 35 percent).Base saturation in mostUltisols decreases withdepth.
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
20/43
The central concept of
Vertisols is that of soils
that have a high content
of expending clay andthat have at some time
of the year deep wide
cracks. They shrink
when drying and swell
when they become
wetter.
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
21/43
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
22/43
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
23/43
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
24/43
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
25/43
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
26/43
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
27/43
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
28/43
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
29/43
http://www.soils.wisc.edu/courses/SS325/boundary.gif -
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
30/43
http://www.soils.wisc.edu/courses/SS325/mor
phology.htm
http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&rct=j&q=soil+morphology&source=images&cd=&cad=rja&docid=krziEWgi4-r6ZM&tbnid=EtCkq1_lZe-NcM:&ved=0CAUQjRw&url=http://www.soils.wisc.edu/courses/SS325/morphology.htm&ei=Lfk_Ua8Sgd2QBcvegcAL&psig=AFQjCNFcbz6QQRLyv8WoDibiwV8tZWbfvQ&ust=1363233298235042http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&rct=j&q=soil+morphology&source=images&cd=&cad=rja&docid=krziEWgi4-r6ZM&tbnid=EtCkq1_lZe-NcM:&ved=0CAUQjRw&url=http://www.soils.wisc.edu/courses/SS325/morphology.htm&ei=Lfk_Ua8Sgd2QBcvegcAL&psig=AFQjCNFcbz6QQRLyv8WoDibiwV8tZWbfvQ&ust=1363233298235042 -
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
31/43
Sizing Up SoilStructure | ColbyDigsSoilcolbydigssoil.c
om
http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&source=images&cd=&docid=da3j_52OgbuLZM&tbnid=cUBQ18Dfz-IvqM&ved=0CAYQjhw&url=http://colbydigssoil.com/2012/07/09/sizing-up-soil-structure/&ei=V4o7U7rHGoSKrgeG-YHQDw&psig=AFQjCNHiJgm6f6887miU-OW1dC20Cru2OA&ust=1396497367541470http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&source=images&cd=&docid=da3j_52OgbuLZM&tbnid=cUBQ18Dfz-IvqM&ved=0CAYQjhw&url=http://colbydigssoil.com/2012/07/09/sizing-up-soil-structure/&ei=V4o7U7rHGoSKrgeG-YHQDw&psig=AFQjCNHiJgm6f6887miU-OW1dC20Cru2OA&ust=1396497367541470http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&source=images&cd=&docid=da3j_52OgbuLZM&tbnid=cUBQ18Dfz-IvqM&ved=0CAYQjhw&url=http://colbydigssoil.com/2012/07/09/sizing-up-soil-structure/&ei=V4o7U7rHGoSKrgeG-YHQDw&psig=AFQjCNHiJgm6f6887miU-OW1dC20Cru2OA&ust=1396497367541470http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&source=images&cd=&docid=da3j_52OgbuLZM&tbnid=cUBQ18Dfz-IvqM&ved=0CAcQjB0&url=http://colbydigssoil.com/2012/07/09/sizing-up-soil-structure/&ei=V4o7U7rHGoSKrgeG-YHQDw&psig=AFQjCNHiJgm6f6887miU-OW1dC20Cru2OA&ust=1396497367541470http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&source=images&cd=&docid=da3j_52OgbuLZM&tbnid=cUBQ18Dfz-IvqM&ved=0CAcQjB0&url=http://colbydigssoil.com/2012/07/09/sizing-up-soil-structure/&ei=V4o7U7rHGoSKrgeG-YHQDw&psig=AFQjCNHiJgm6f6887miU-OW1dC20Cru2OA&ust=1396497367541470http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&source=images&cd=&docid=da3j_52OgbuLZM&tbnid=cUBQ18Dfz-IvqM&ved=0CAYQjhw&url=http://colbydigssoil.com/2012/07/09/sizing-up-soil-structure/&ei=V4o7U7rHGoSKrgeG-YHQDw&psig=AFQjCNHiJgm6f6887miU-OW1dC20Cru2OA&ust=1396497367541470http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&source=images&cd=&docid=da3j_52OgbuLZM&tbnid=cUBQ18Dfz-IvqM&ved=0CAcQjB0&url=http://colbydigssoil.com/2012/07/09/sizing-up-soil-structure/&ei=V4o7U7rHGoSKrgeG-YHQDw&psig=AFQjCNHiJgm6f6887miU-OW1dC20Cru2OA&ust=1396497367541470http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&source=images&cd=&docid=da3j_52OgbuLZM&tbnid=cUBQ18Dfz-IvqM&ved=0CAcQjB0&url=http://colbydigssoil.com/2012/07/09/sizing-up-soil-structure/&ei=V4o7U7rHGoSKrgeG-YHQDw&psig=AFQjCNHiJgm6f6887miU-OW1dC20Cru2OA&ust=1396497367541470http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&source=images&cd=&docid=da3j_52OgbuLZM&tbnid=cUBQ18Dfz-IvqM&ved=0CAcQjB0&url=http://colbydigssoil.com/2012/07/09/sizing-up-soil-structure/&ei=V4o7U7rHGoSKrgeG-YHQDw&psig=AFQjCNHiJgm6f6887miU-OW1dC20Cru2OA&ust=1396497367541470http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&source=images&cd=&docid=da3j_52OgbuLZM&tbnid=cUBQ18Dfz-IvqM&ved=0CAcQjB0&url=http://colbydigssoil.com/2012/07/09/sizing-up-soil-structure/&ei=V4o7U7rHGoSKrgeG-YHQDw&psig=AFQjCNHiJgm6f6887miU-OW1dC20Cru2OA&ust=1396497367541470http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&source=images&cd=&docid=da3j_52OgbuLZM&tbnid=cUBQ18Dfz-IvqM&ved=0CAYQjhw&url=http://colbydigssoil.com/2012/07/09/sizing-up-soil-structure/&ei=V4o7U7rHGoSKrgeG-YHQDw&psig=AFQjCNHiJgm6f6887miU-OW1dC20Cru2OA&ust=1396497367541470http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&source=images&cd=&docid=da3j_52OgbuLZM&tbnid=cUBQ18Dfz-IvqM&ved=0CAYQjhw&url=http://colbydigssoil.com/2012/07/09/sizing-up-soil-structure/&ei=V4o7U7rHGoSKrgeG-YHQDw&psig=AFQjCNHiJgm6f6887miU-OW1dC20Cru2OA&ust=1396497367541470http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&source=images&cd=&docid=da3j_52OgbuLZM&tbnid=cUBQ18Dfz-IvqM&ved=0CAYQjhw&url=http://colbydigssoil.com/2012/07/09/sizing-up-soil-structure/&ei=V4o7U7rHGoSKrgeG-YHQDw&psig=AFQjCNHiJgm6f6887miU-OW1dC20Cru2OA&ust=1396497367541470http://www.google.com/url?sa=i&source=images&cd=&docid=da3j_52OgbuLZM&tbnid=cUBQ18Dfz-IvqM&ved=0CAYQjhw&url=http://colbydigssoil.com/2012/07/09/sizing-up-soil-structure/&ei=V4o7U7rHGoSKrgeG-YHQDw&psig=AFQjCNHiJgm6f6887miU-OW1dC20Cru2OA&ust=1396497367541470 -
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
32/43
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
33/43
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
34/43
Angular blocky
Crumb
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
35/43
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
36/43
Differentsoil color
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
37/43
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
38/43
http://www.nativerevegetation.org/learn/manual/ch_5.aspx
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
39/43
Soil consistency Roots
pH and effervescence Special feature
Moisture status Consistence Abbreviation DescriptionAlmost no natural adhesion
Table 9.7.1. Classification of consistence (Buol et al., 1997).R f
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
40/43
wet Nonsticky wsoAlmost no natural adhesionof soil material to fingers
Slightly sticky wssSoil material adheres to onlyone finger
Sticky wsSoil material adheres to bothfingers
Very sticky wvs Soil material strongly adheresto both fingers
Nonplastic wpoNo wire is formable by rollingmaterial between the hands
Slightly plastic wpsOnly short (< 1cm) wires areformed by rolling materialbetween the hands
Plastic wp
Long wires (>1cm) can beformed and moderatepressure is needed to deforma block of the moldedmaterial
Very plastic wvpMuch pressure is needed todeform a block of the moldedmaterial
Moist Loose ml Soil material is noncoherent
Very friable mvfrAggregates crush easilybetween thumb and finger
Friable mfrGentle pressure is required tocrush aggregates
Firm mfiModerate pressure is requiredto crush aggregates
Very firm mvfi Strong pressure is required tocrush aggregates
Reference
Table 9.8.1. Classification of roots.
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
41/43
Root quantity classes Per unit area
Very few < 0.2
Moderately few 0.2 to 1
Few < 1
Common 1 to < 5
Many >= 5
Size classes of roots Diameter in mm
Very fine < 1
Fine 1 - 2
Medium 2 - 5
Coarse 5 - 10
Very coarse > 10
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
42/43
Small precipitates (e.g. salts, carbonates) dispersedthroughout the matrix of a horizon
Concentrations
Masses:
Noncemented bodies of accumulation of variousshapes that cannot be removed as discrete units (e.g.
crystalline salts)
Nodules:
Cemented bodies of various shapes that can beremoved as discrete units from soil
-
8/12/2019 c - Morfologi Tanah Dit
43/43
Concretions: Cemented bodies similar to nodules, except for
the presence of visible, concentric layers of
material around a point, line, or plane Crystals: Macro-crystalls forms of relatively soluble salts
(e.g. gypsum, carbonates) that form in situ byprecipitation from soil solution
Biological concentrations: Discrete bodies accumulated by a biological
process (e.g., fecal pellets, insect casts)